
VM can be configured to use alternative hostname Hosts file modification is restricted, impossible or In more restrictive environments, where DNS record or Hostname resolution can use any of the standard OS-provided Must be resolvable from all cluster nodes, as wellĪs machines on which command line tools such as rabbitmqctl RabbitMQ nodes address each other using domain names,Įither short or fully-qualified (FQDNs). Cluster Formation Requirements Hostname Resolution If a system uses fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) for hostnames, RabbitMQ nodesĪnd CLI tools must be configured to use so called long node names.įor server nodes this is done by setting the RABBITMQ_USE_LONGNAME environment variableįor CLI tools, either RABBITMQ_USE_LONGNAME must be set or the -longnames option The node resolves its hostname and prepends rabbit to it to compute its node name.
Via the RABBITMQ_NODENAME environment variable. When a node starts up, it checks whether it has been assigned a node name. That the hostname part of every node name must resolve.ĬLI tools also identify and address nodes using node names. and a cluster, nodes identify and contact each other using node names. (this is usually the case in development and QA environments), they must useĭifferent prefixes, e.g. If more than one node is running on a given host For example, a node name with the prefix of rabbit and hostname of. A node name consists of two parts,Ī prefix (usually rabbit) and hostname. RabbitMQ nodes are identified by node names.
Subsequently turned back into individual brokers again. These nodes can be joined into clusters, and The composition of a cluster can be altered dynamically.Īll RabbitMQ brokers start out as running on a single Please refer to the Cluster Formation guide for details.
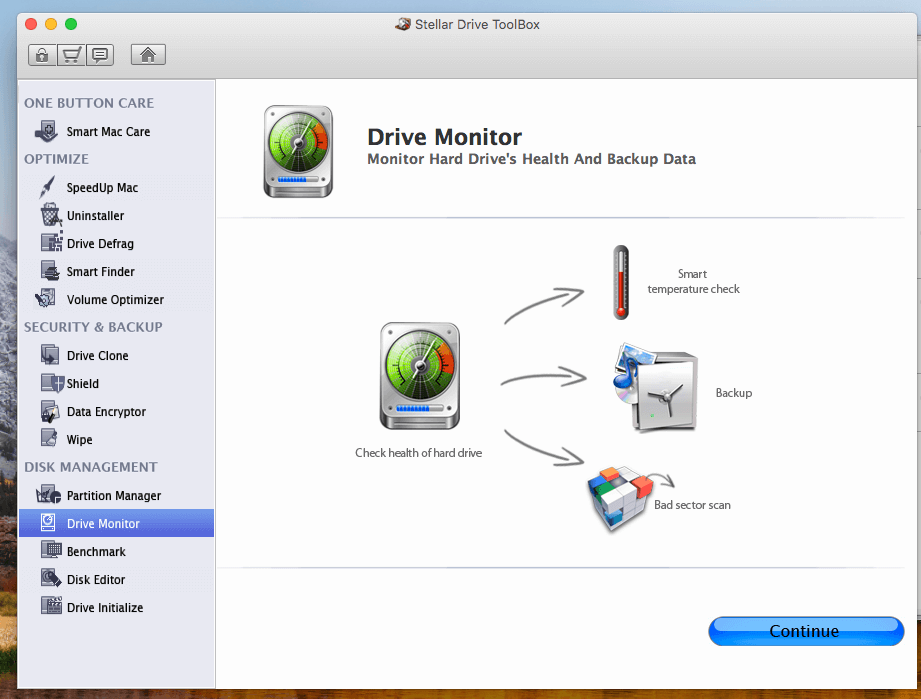
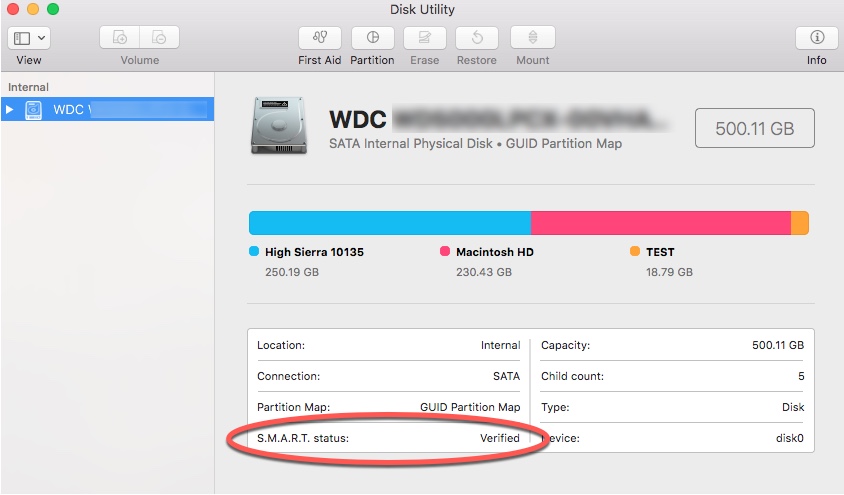
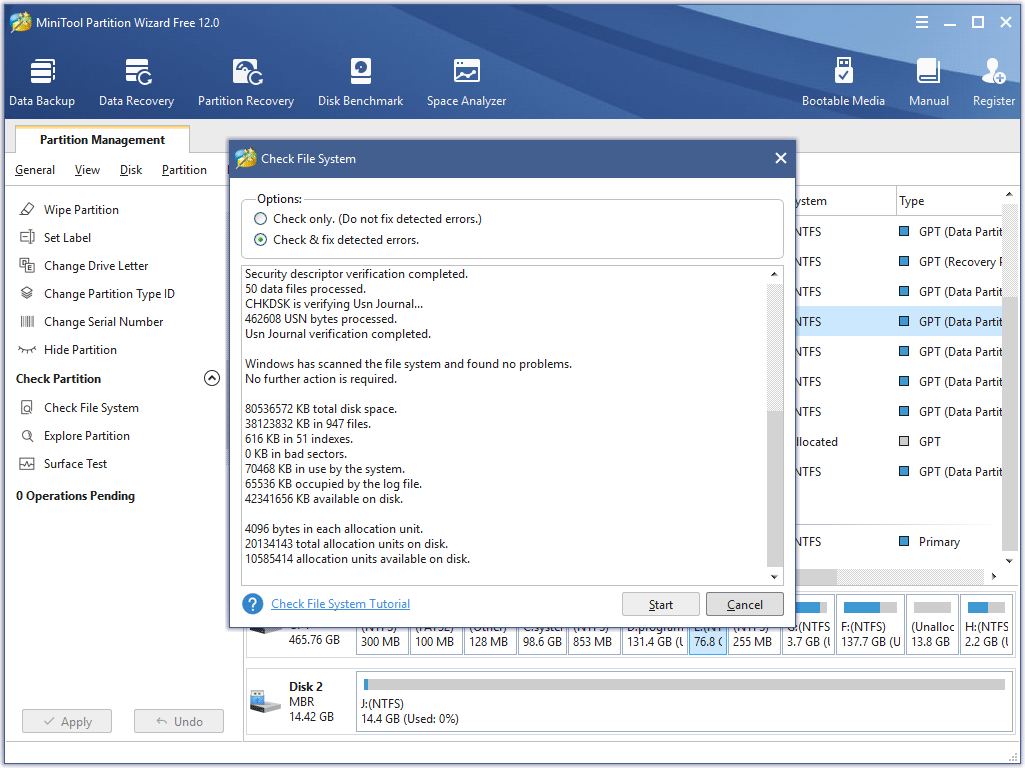
Tool in mac os x checks for bad clusters in the hard disk. how to#
How to reset a cluster node to a pristine (blank) stateĪnd more.Node readiness probes and how they can affect rolling cluster restarts.Node restarts and how nodes rejoin their cluster.Why it's important to use an odd number of nodes and two cluster nodes are highly recommended against.How nodes authenticate to each other (and with CLI tools).What data is and isn't replicated between cluster nodes.How RabbitMQ nodes are identified: node names.This guide covers fundamental topics related to RabbitMQ clustering:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
